Imagine not being able to enjoy a meal with your loved ones or struggling to swallow even the simplest of foods. This is the reality for millions of people living with dysphagia, a condition that impacts the ability to swallow properly. In this post, we’ll explore the impact of dysphagia on nutrition and overall health and discuss some strategies to manage this challenging condition.
Understanding Dysphagia
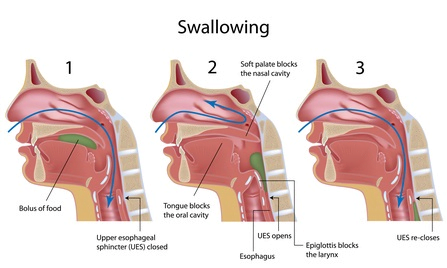
Dysphagia refers to the difficulty or discomfort experienced when swallowing food, liquids, or even saliva. It can occur at any age and may result from various causes, including neurological disorders, muscular conditions, structural abnormalities, or even certain medications. The consequences of dysphagia can be far-reaching, affecting both physical and emotional wellbeing.
Impact on Nutrition
Dysphagia poses significant challenges when it comes to nutrition. This inability to swallow properly can lead to inadequate intake of essential nutrients, minerals, and vitamins. This can result in weight loss, malnutrition, and compromised immune function. Plus, the fear of choking or aspiration can cause individuals with dysphagia to restrict their food intake, further exacerbating nutritional deficiencies. IV hydration services are increasingly being utilized to address these nutritional gaps, providing a direct and efficient way to deliver essential nutrients and hydration to those struggling with dysphagia. By supplementing their diet with IV hydration in Boston, individuals can better manage their nutritional needs and support overall health.”
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Dysphagia not only affects physical health but also takes a toll on emotional wellbeing. Difficulties with swallowing can cause frustration, embarrassment, and anxiety – particularly in social settings. The fear of choking or being unable to communicate effectively during meals can lead to social isolation and a decline in overall quality of life. It is essential to address the psychological impact of dysphagia and provide support to individuals and their caregivers.
Managing Dysphagia
While dysphagia can be a challenging condition to live with, the good news is that there are strategies and interventions that can help improve swallowing function and ensure adequate nutrition.
1 – Dietary Modifications
One of the key approaches to managing dysphagia is making dietary modifications. Depending on the severity and underlying cause of dysphagia, a speech-language pathologist or dietician may recommend specific textures or consistencies of food and beverages. These modifications can include pureed, minced, or chopped foods, along with using products like Simply Thick dysphagia gel to make swallowing liquids easier and safer.
2 – Swallowing Exercises
Along with dietary modifications, swallowing exercises can play an essential role in improving swallowing function. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing and improve coordination. Working with a speech-language pathologist or a dysphagia therapist can help individuals with dysphagia learn and practice these exercises effectively.
3 – Assistive Devices
Various assistive devices can be used to aid in managing dysphagia and promoting safe swallowing. These devices can include special spoons, cups, or straws that facilitate controlled delivery of food and liquids. Plus, there are various oral-motor exercises and tools that can assist with strengthening the muscles involved in swallowing.
4 – Collaboration with Healthcare Professionals
It’s important for individuals with dysphagia to work closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including speech-language pathologists, dieticians, physicians, and occupational therapists. These professionals can provide tailored recommendations, monitor progress, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
5 – Support and Education
Living with dysphagia can be overwhelming, but support and education are available. Joining support groups or seeking counseling can provide emotional support and help individuals and their caregivers navigate the challenges associated with dysphagia. Plus, educational resources and workshops can provide valuable information on managing dysphagia and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
6 – Maintaining Hydration
Dysphagia can also impact hydration levels, as individuals may find it challenging to consume enough fluids. Dehydration can lead to various health complications, so it’s crucial to address this issue. Strategies to promote hydration include offering thickened liquids or using special cups with controlled flow rates. Plus, incorporating hydrating foods like fruits, vegetables, and soups can contribute to overall hydration.
7 – Alternative Feeding Options
In cases where dysphagia is severe or does not improve with conservative measures, alternative feeding options may be considered. These options include enteral nutrition, where nutrients are delivered directly to the stomach or intestines through a feeding tube, or parenteral nutrition, which involves receiving nutrients intravenously. These approaches ensure adequate nutrition while bypassing the swallowing difficulties.
8 – Prevention and Safety Measures
Prevention and safety measures are crucial in minimizing the risk of complications associated with dysphagia. This includes maintaining good oral hygiene to reduce the likelihood of infections, practicing proper positioning during means to facilitate swallowing, and avoiding distractions and rushed eating to promote focused, controlled swallowing. Implementing these measures can significantly reduce the chances of choking or aspiration.
Dysphagia can have a profound impact on nutrition and health, impacting both physical and emotional wellbeing. However, with the right strategies, support, and collaboration with healthcare professionals, individuals with this condition can maintain a fulfilling and healthy lifestyle.